| Page 1 out of 51 Pages |
Refer to the exhibit.
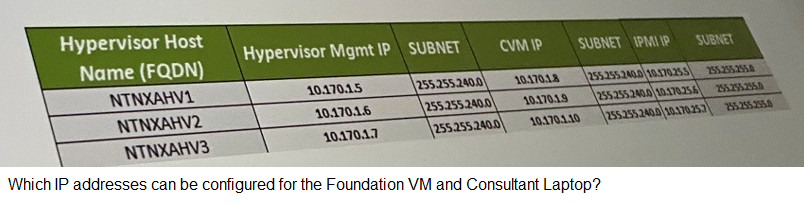
A. FVM: 10.170.25.15/24, Laptop: 10.170.25.16/24
B. FVM: 10.170.1.2/20, Laptop: 10.170.1.12/20
C. FVM: 10.170.16.15/20,: 10.170.16.16/20
D. FVM: 10.170.25.2/24, Laptop: 10.170.25.12/24
Explanation: Based on the subnet assignments from the exhibit provided, the Hypervisor Management IP addresses fall within the 10.170.0.5, 10.170.0.6, 10.170.0.7 range with a subnet mask of 255.255.240.0, indicating a /20 subnet. However, the Foundation VM (FVM) and the Consultant Laptop should ideally be on the same subnet as the Controller Virtual Machine (CVM) to facilitate easy access and management. The CVM IP addresses indicated are 10.170.0.4, 10.170.0.9, and 10.170.0.10 with subnet 255.255.240.0 (/20). Thus, the appropriate choice for the FVM and Laptop that matches the subnet without overlapping with existing IPs and allows network configuration without conflicts would be in the same /24 range as suggested in option D, i.e., FVM: 10.170.25.2/24, Laptop: 10.170.25.12/24.
An administrator recently added in 3 nodes to an existing 5 node cluster. While 1 node came with its own block, the other 2 nodes where added to an existing share. After adding the nodes, the administrator sees that the hardware tab displays the correct number of nodes, but incorrect position in the diagram tab. What should the administrator do to resolve the issue?
A. Check the factory_config.json for all 3 nodes
B. SSH into CVM and perform genesis restart on each CVM
C. SSH into the CVMs and run genesis acropolis stop; cluster start
D. Check the factory_config. json for the two single nodes.
Explanation: When nodes are added to a Nutanix cluster and there is a discrepancy in the position or configuration as shown in the hardware diagram tab, it's essential to check the factory_config.json file on all newly added nodes. This file contains important configuration details that define how each node is identified and operates within the cluster. Incorrect or inconsistent settings in the factory_config.json can lead to display and configuration errors in the Prism interface. Correcting any discrepancies in this file will help resolve issues with node identification and display in the diagram tab.
A consultant has been tasked with increasing security on a Nutanix cluster by disabling password authentication when accessing the CVM and AHV hosts and instead moving to key-based SSH. What is the easiest way for the consultant to meet these requirements?
A. Enable STlGs via command line on SSH to a CVM.
B. Configure LDAP authentication through a secure server.
C. Enable Cluster Lockdown and provide an RSA key.
D. Restrict access with User Management in Prism.
Explanation:
The most straightforward approach for increasing security by disabling password authentication and moving to key-based SSH on a Nutanix cluster involves:
C. Enable Cluster Lockdown and provide an RSA key: Cluster Lockdown mode
restricts management access to the cluster, ensuring that only key-based SSH
authentication is used to access the CVM and AHV hosts, enhancing security by
eliminating the use of passwords.
A consultant is unable to install virtualization software on a laptop. Which two versions of Foundation can be used to resolve this issue? (Choose two.)
A. Foundation VM
B. Foundation Portable
C. Foundation Central
D. Foundation Applet
Explanation: When a consultant is unable to install virtualization software on a laptop, the most suitable versions of Foundation to resolve this issue would be Foundation Portable (Option B) and Foundation Applet (Option D). Both these versions are designed to be used in environments where installing additional virtualization software might not be feasible. Foundation Portable can be run from a USB drive, and the Foundation Applet is a Javabased tool that can run directly on a host machine without the need for a full virtual machine environment.
An administrator has a VM that consumes large amounts of storage and has the following
characteristics:
• Create large / sequential writes
• Data must be kept for years
• Data is normally only accessed at the end of the year to run report
The administrator decides to use Erasure Coding to save space.
Which feature should the administrator utilize to save space for this VM?
A. Inline Compression
B. Flash Mode
C. Cache Dedup
D. Post-Process Compression
Explanation:
Erasure coding is a method of data protection in which data is broken into fragments,
expanded and encoded with redundant data pieces, and stored across a set of different
locations or storage media. The goal of erasure coding is to enable data that becomes
corrupted at some point in the disk storage process to be reconstructed by using
information about the data that’s stored elsewhere in the array1.
In the context of Nutanix, erasure coding increases the usable capacity on a cluster.
Instead of replicating data, erasure coding uses parity information to rebuild data in the
event of a disk failure1. The capacity savings of erasure coding is in addition to
deduplication and compression savings1.
Given the characteristics of the VM in the question (large/sequential writes, data kept for
years, data accessed only at the end of the year), Post-Process Compression would be the
most suitable feature to utilize to save space. This is because Post-Process Compression,
as the name suggests, compresses data after it has been written to the storage, which is
suitable for data that is not accessed frequently2.
A customer is deploying Nutanix AHV clusters over hundreds of remote sites worldwide. Prism Central will be used to centrally manage all clusters. Customer security policy requires the use of MS Active Directory (AD).groups to authenticate all network devices. Which method should be consultant use to meet the requirements?
A. Integrate AD authentication on all CVMs.
B. Integrate AD authentication on Prism Central Only.
C. Proxy Prism Element traffic through Prism Central.
D. Integrate AD authentication on all Prism Element Clusters.
Explanation: When managing multiple Nutanix AHV clusters across various locations with a centralized management through Prism Central, it is essential to secure each cluster individually. Integrating Microsoft Active Directory authentication directly on all Prism Element clusters allows each site to independently authenticate users while still being centrally managed. This method aligns with security policies that require network devices to authenticate via AD groups, ensuring that local administrative actions at each site are also secured under the same policy.
| Page 1 out of 51 Pages |
The Nutanix Certified Services Core Infrastructure Professional (NCS-Core) exam validates your ability to deliver professional services, handle Nutanix solutions efficiently, and apply core infrastructure concepts in real-world environments. As demand rises for experts in hyperconverged and multi-cloud systems, this credential sets you apart as a reliable and certified Nutanix professional.
This guide covers the exam overview, preparation tips, job outlook, salary insights, benefits, and why practice questions are your best preparation weapon.

Pro Tip: Set a clear study schedule and break topics into small daily tasks to stay consistent and avoid burnout.
| Detail | Information |
|---|---|
| Exam Code | NCS-Core |
| Number of Questions | 60 |
| Question Format | Multiple-choice and scenario-based |
| Time Limit | 120 minutes |
| Passing Score | 70% |
| Delivery | Online proctored |
While no formal prerequisites are required, it is highly recommended that candidates have:
The NCS-Core exam is ideal for IT professionals who:
This certification is especially valuable for those aiming to advance into senior engineering or consulting positions.
| Skill Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Cluster Deployment | Install and configure Nutanix clusters |
| Storage Management | Set up and manage storage containers and volumes |
| Virtualization | Manage virtual machines and hypervisors |
| Data Protection | Configure backups, replication, and disaster recovery |
| Monitoring & Troubleshooting | Monitor system health and resolve issues |
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Exam Familiarity | Understand question styles and test flow |
| Identify Weak Areas | Spot topics needing extra review |
| Time Management | Practice pacing for the 120-minute exam |
| Boost Confidence | Reduce anxiety with realistic exam rehearsal |
| Improve Pass Rate | Increase first-attempt success likelihood |
| Candidate | Role | Challenge Identified | Strategy Used | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amit | Cloud Engineer | Backup configuration gaps | Focused on data protection practice sets | Passed with 88% |
| Sophia | Systems Administrator | Weak VM management | Spent extra hours on Prism Element labs | Passed confidently |
| Group | Pass Rate | Avg. Study Time | Retake Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Used Practice Tests | 90-95% | 3-4 weeks | 5-10% |
| No Practice Tests | 50-60% | 6-8 weeks | 40-50% |
| Job Title | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutanix Consultant | Deliver professional services and solution design |
| Cloud Infrastructure Engineer | Manage multi-cloud and hyperconverged deployments |
| Systems Engineer | Implement and monitor Nutanix clusters |
| IT Project Lead | Oversee Nutanix implementations in enterprise environments |
| Region | Estimated Salary Range |
|---|---|
| USA | $85,000 – $120,000/year |
| UK | £50,000 – £75,000/year |
| India | ₹900,000 – ₹1,500,000/year |